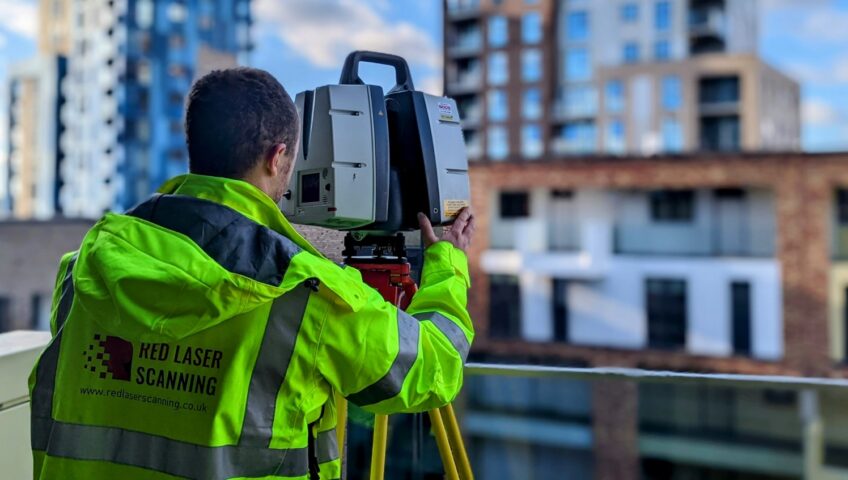
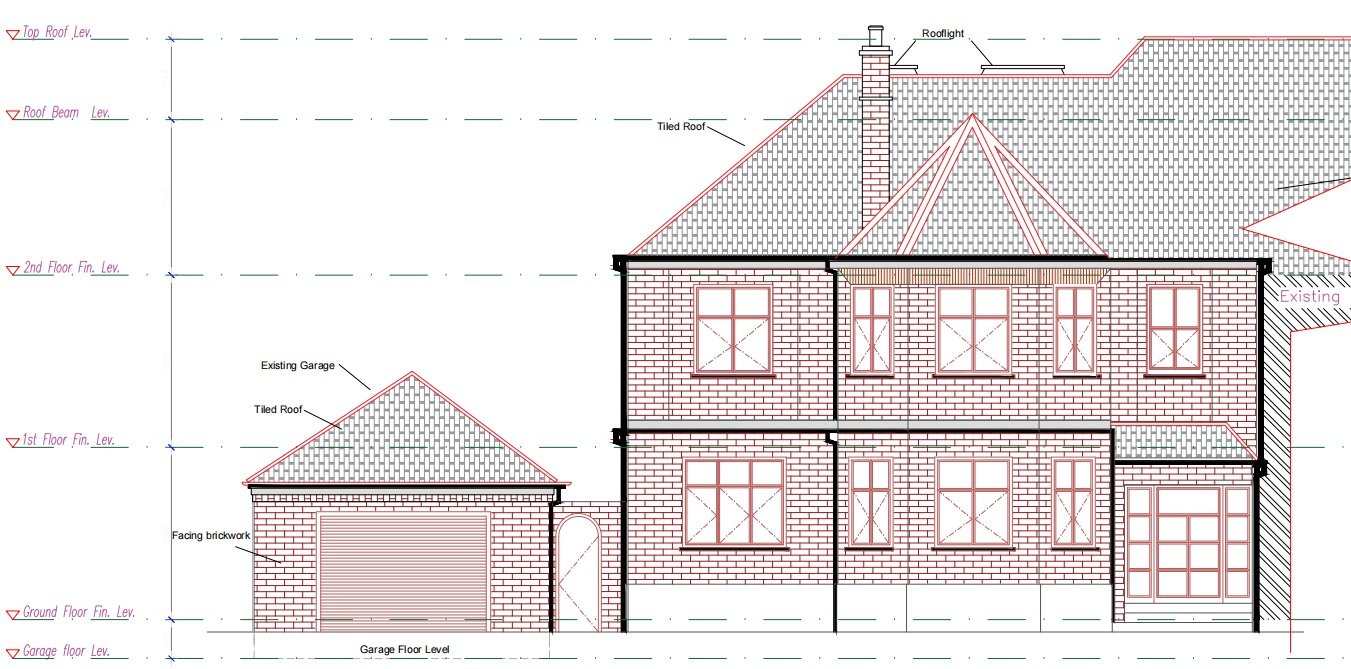
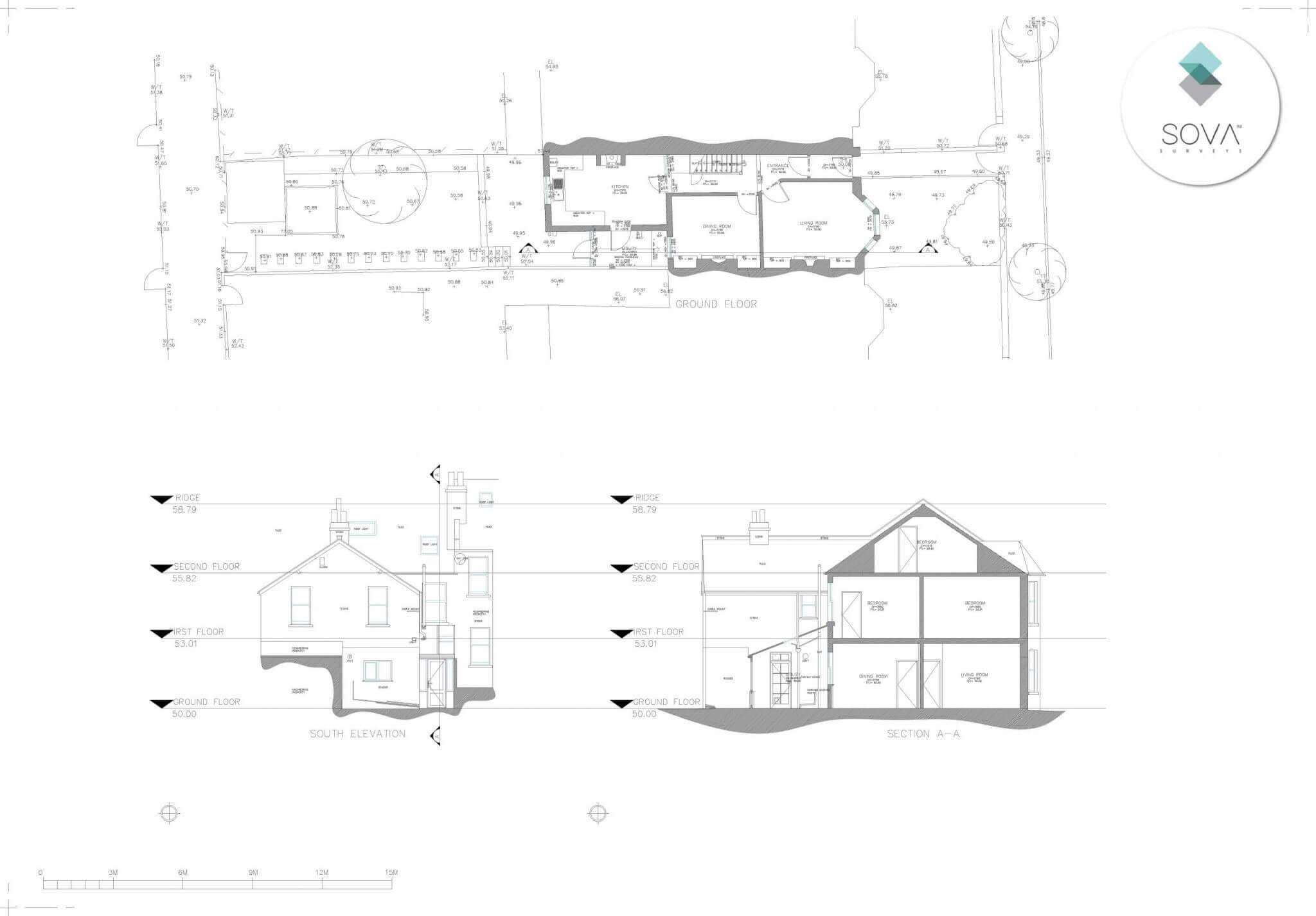
In the realm of measured building survey services, precision is paramount. These surveys are essential for countless projects, providing crucial data for design, construction, and renovation. However, not all surveys are created equal, and opting for cheaper options can lead to costly mistakes.
The Importance of Precision in Measured Building Surveys
High-precision building surveys require exacting accuracy. Whether capturing floor plans, elevations, or intricate architectural details, precision is essential. Each measurement must be meticulously recorded to ensure data integrity and project success.
Imagine if inaccuracies are overlooked—a minor measurement discrepancy could lead to significant setbacks in construction, causing delays, rework, and additional costs.
Reliability: The Backbone of Effective Surveys
Reliability is the cornerstone of any reputable surveying service. Without reliable surveying solutions, even the most precise measurements are useless. Reliable surveys instil confidence, assuring stakeholders that the data is trustworthy for critical decisions.
Conversely, unreliable surveys introduce uncertainty, casting doubts over project timelines and budgets. Relying on flawed data for construction efforts is risky, with potential errors around every corner.
Quality Over Cost: Why Cheaper Surveys Are a Risky Investment
In today’s cost-conscious world, cheaper surveys can be tempting. However, prioritising cost over quality is a gamble. While cheaper surveys might offer short-term savings, they often lead to hidden costs and risks that outweigh the initial investment.
Geo Scan, a trusted leader in professional surveying services, understands the dangers of sacrificing quality for cost savings. With a commitment to precision, reliability, and quality assurance, Geo Scan delivers results that stand the test of time.
The Geo Scan Advantage: Delivering Uncompromising Quality, Reliability, and Precision
At Geo Scan, precision is not just a goal—it’s a promise. Our team of experienced professionals uses cutting-edge technology and rigorous quality control to ensure every survey meets the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.
Our track record speaks for itself. Countless satisfied clients have trusted Geo Scan with their most demanding projects, knowing we deliver results that exceed expectations.
Conclusion
In the world of accurate building surveys, quality is crucial. Choosing precision over price is a smart investment. By partnering with a trusted provider like Geo Scan, you can ensure your project is in capable hands, with reliable results.
Next time you’re tempted by cheaper surveys, remember: when it comes to precision, there’s no substitute for quality. Choose Geo Scan and experience the difference.
Contact Geo Scan today to learn more about our industry-leading surveying services.
FAQ Section
1. What is a Measured Building Survey?
Measured building surveys are comprehensive assessments of a building’s structure and features. They provide precise data on floor plans, elevations, and architectural details, which are crucial for any design, construction, or renovation project. Think of them as the foundation of your project’s success—ensuring that every detail is captured accurately.
2. Why Is Precision Important in your Measured Building Survey?
Precision in measured building surveys is essential because even minor measurement errors can cause significant issues. For instance, a small discrepancy can lead to delays, increased construction costs, and even structural problems. Accurate surveys ensure data integrity, helping you avoid these costly mistakes and keeping your project on track.
3. What Are the Risks of Using Cheaper Surveying Services?
Opting for cheaper surveying services can be risky. These services might cut corners on accuracy and reliability, leading to flawed data. Imagine relying on incorrect measurements—this could result in construction errors, project delays, and additional costs for rework. Investing in high-quality surveying services ensures you get reliable and precise data, which is vital for any project’s success.
4. How Does Geo Scan Ensure the Accuracy of Their Surveys?
Geo Scan prioritises accuracy by using advanced surveying technology and implementing strict quality control processes. Our team of experienced professionals meticulously records each measurement, ensuring that every detail is precise. This commitment to excellence has made Geo Scan a trusted leader in the field of professional building surveying services.
5. What Should I Look for in a Professional Surveying Service?
Answer: When choosing a professional surveying service, look for a company known for its accuracy, reliability, and quality. Ensure they use state-of-the-art technology and have a team of
experienced surveyors. Quality surveys can save you from costly mistakes and ensure your project is completed successfully. Always opt for a service that prioritises precision and has a proven track record.