[
Applications Innovantes De La Technologie De Scan 3D Laser

Executive Summary

La technologie de scan 3D laser révolutionne de nombreux secteurs en apportant précision, rapidité et finesse dans la capture de formes et de structures complexes. À travers cet article, nous explorons comment cette technologie s’insinue dans des domaines variés, allant de la médecine à l’architecture, en passant par la fabrication et l’art. Que vous soyez professionnel ou simplement curieux, découvrez comment l’innovation dans le scan 3D laser ouvre des portes insoupçonnées et transforme nos méthodes de travail, de création et de compréhension du monde qui nous entoure.
Introduction
Le scan 3D laser est une technologie qui capture avec une précision extrême la forme et la texture d’objets ou d’environnements réels en utilisant des faisceaux laser. En quelques années, elle est devenue un outil indispensable dans de nombreux domaines où la précision et la rapidité sont essentielles. Son efficacité et ses applications éclectiques en font une avancée technologique qui continue de repousser les limites de ce qui est possible.
FAQ
Q1 : Qu’est-ce que le scan 3D laser ?
Le scan 3D laser consiste à utiliser un laser pour capturer la géométrie d’un objet ou d’un espace. La technologie génère un nuage de points 3D précis qui peut être transformé en modèles numériques détaillés.
Q2 : Quels sont les principaux domaines d’application ?
Ceux-ci incluent l’architecture, la médecine, la fabrication, l’art, la recherche archéologique, la maintenance industrielle, et bien d’autres.
Q3 : Quelles sont les limites du scan 3D laser ?
Les limites concernent la performance en environnement très lumineux ou poussiéreux, la complexité de certains matériaux avec des surfaces très réfléchissantes ou absorbantes, et le coût élevé de certains équipements haut de gamme.
Technological Advancements and Benefits
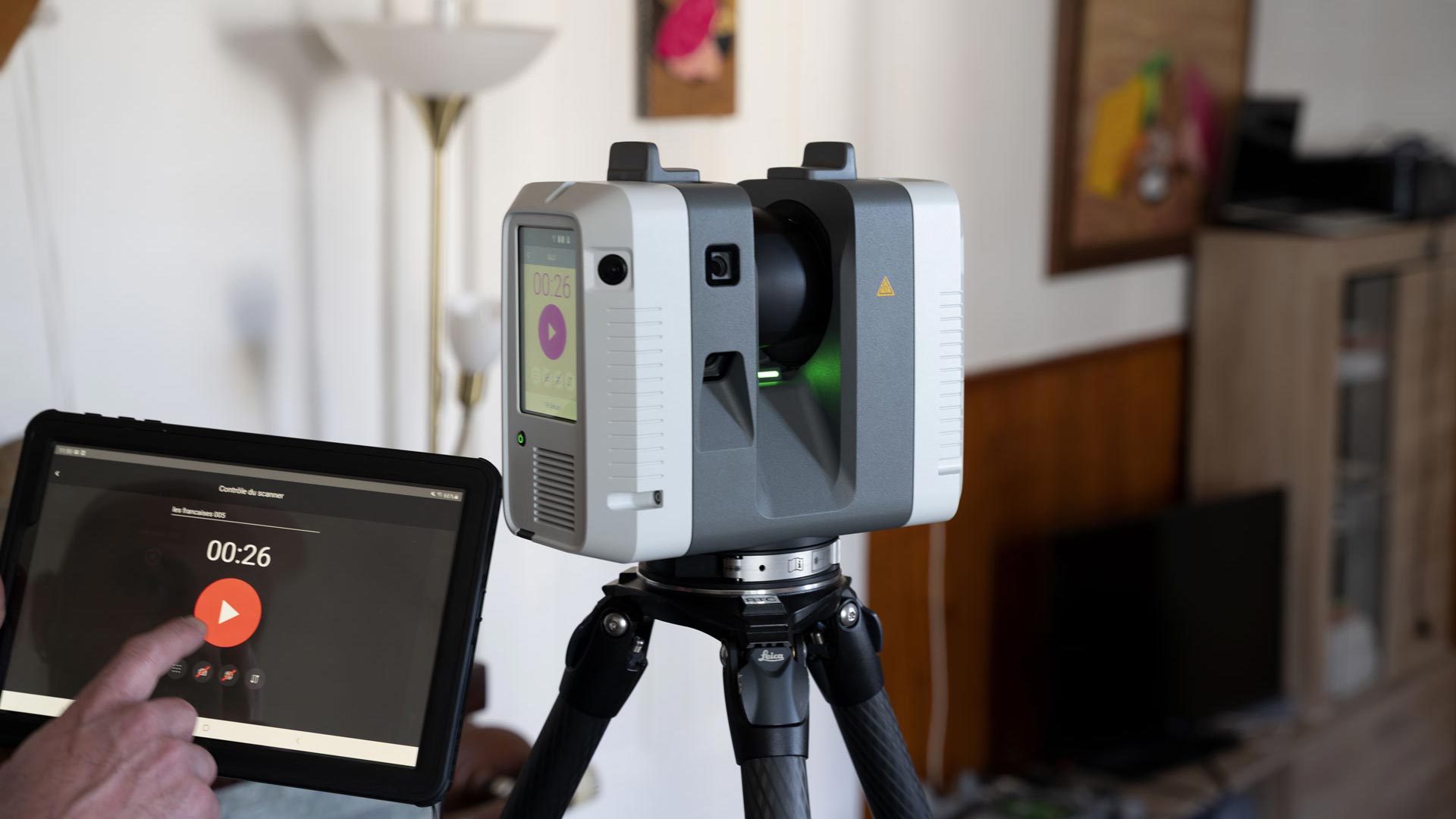
Le développement de la technologie de scan 3D laser a suivi une courbe ascendante, avec des améliorations notables dans la précision, la vitesse et l’accessibilité. Elle permet désormais de réaliser des scans en quelques minutes, offrant une grande précision — souvent jusqu’à la fraction de millimètre. Ces avancées ont permis une démocratisation de la technologie, rendant ses applications plus accessibles et plus utiles pour une utilisation quotidienne et professionnelle.
- Haute résolution: La capacité à capturer des détails extrêmes pour des reproductions fidelisées, notamment dans la conservation culturelle ou la médecine.
- Vitesse remarquable: Réaliser des scans en quelques secondes ou minutes, ce qui optimise le temps de projet.
- Facilité d’utilisation: Interfaces intuitives permettant aux non-spécialistes de maîtriser la technologie.
- Fusion avec autres outils: S’intégrer avec la réalité augmentée, la modélisation CAD, ou la réalité virtuelle pour des projets hyper réalistes.
- Application mobile: Des scanners portables permettent d’effectuer des captures sur le terrain sans besoin d’un post-traitement complexe.
Top 5 Subtopics
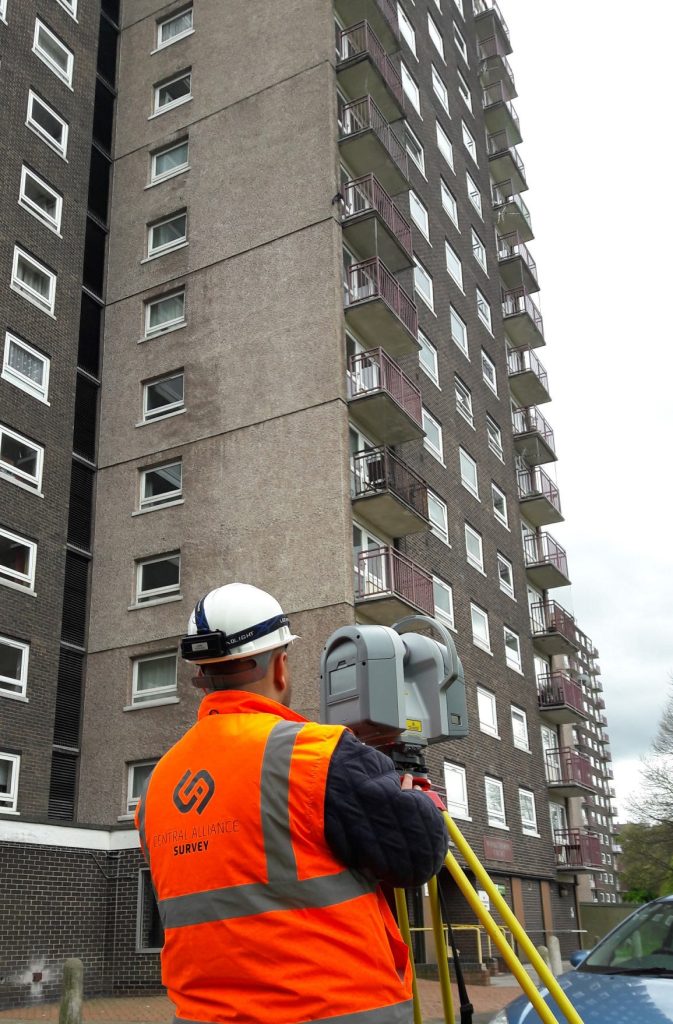
La Contribution de la Technologie de Scan 3D Laser en Architecture et Architecture Intérieure
Dans ce domaine, le scan laser permet de créer des modèles très précis de bâtiments existants, facilitant la restauration, la rénovation ou la planification structurale. Avec cette technologie, la modélisation de bâtiments historiques ou complexes devient plus accessible et fiable.
- Relevé précis de structures anciennes et complexes : Permet de préserver le détail historique sans perte d’informations.
- Planification de rénovations : Facilite le développement de plans précis, évitant erreurs et approximations.
- Création de modèles numériques pour la visualisation : Permet aux clients et aux architectes de voir le projet final en réalité virtuelle.
- Maintenance prédictive : Surveille l’état des structures pour anticiper des défaillances.
- Optimisation de la construction : Réduit le gaspillage en permettant une meilleure planification et vérification.
La Révolution de la Médecine avec le Scan 3D Laser
Dans le secteur médical, cette technologie permet de réaliser des modèles anatomiques précis à partir de scans, facilitant la planification chirurgicale, la fabrication de prothèses sur mesure, ou même la fabrication d’implants.
- Imagerie détaillée pour la chirurgie : Permet une planification précise et moins invasive.
- Prothèses parfaitement adaptées : Des modèles sur mesure qui améliorent le confort et l’efficacité.
- Réduction des risques opératoires : Visualisation préalable pour éviter les erreurs.
- Fabrication de modèles anatomiques : Enseignement ou préparation pour des interventions complexes.
- Suivi médical précis : Surveille l’évolution des patients avec des données exactes.
La Contribution à la Fabrication et à l’Ingénierie
Dans ces secteurs, le scan 3D laser joue un rôle clé dans la conception, la vérification, et la réparation de pièces ou de machines. Il est donc un allié précieux dans l’industrie 4.0, permettant la fabrication additive ou la rétro-ingénierie.
- Reverse engineering (rétro conception) : Reproduire une pièce pour sa réparation ou son amélioration.
- Contrôle qualité en temps réel : Vérifier que les pièces produites respectent précisément le design prévu.
- Prototypage rapide : Accélère le processus de développement de nouveaux produits.
- Maintenance préventive : Identifier les déformations ou usures avant défaillance.
- Fabrication additive : Support dans l’impression 3D pour créer des prototypes ou pièces finales.
Applications dans l’Art et la Conservation du Patrimoine Culturel
L’art et la conservation exploitent la précision du scan laser pour documenter, restaurer, ou même recréer des œuvres d’art. La technologie permet de préserver fidèlement l’authenticité tout en facilitant la restauration ou la reproduction.
- Restauration d’objets fragiles : Répliquer avec précision pour remplacement ou reconstruction.
- Reproduction d’œuvres rares : Facilite la création de copies sans exposer l’original.
- Documentation complète : Mise en archive numérique très détaillée.
- Interactivité et exposition : Créer des expériences immersives en réalité augmentée pour le public.
- Restitution virtuelle : Reconstituer des sites ou objets disparus ou endommagés.
La Transformations de l’Industrie grâce au Scan 3D
Dans l’industrie, cette technologie facilite la digitalisation des processus, améliore l’efficacité, et réduit les coûts grâce à une meilleure gestion des données et à l’automatisation.
- Optimisation de la chaîne de production : Analyse précise en amont pour minimiser le gaspillage.
- Inspection et maintenance : Détection d’anomalies et déformations en phase de révision.
- Intégration avec l’IA : Pour une analyse prédictive ou l’optimisation automatique.
- Design collaboratif : Partage instantané de modèles dans une plateforme collaborative.
- Projet de digital twin : Reproduire en numérique un objet ou un système pour simulations avancées.
Conclusion
L’essor du scan 3D laser ne montre aucun signe de ralentissement, et son impact ne cesse de croître dans tous les secteurs imaginables. La capacité de capturer avec une précision extrême des mondes aussi variés que le patrimoine historique, la médecine, ou l’ingénierie industrielle ouvre un avenir rempli de promesses. En intégrant cette technologie, les professionnels découvrent une source infinie de nouvelles possibilités — pour la création, la conservation, ou l’innovation. La fusion entre le réel et le numérique n’a jamais été aussi fluide, et il est certain que le scan 3D laser continuera de repousser les limites du possible.
Tags
- Impression 3D
- Modélisation numérique
- Conservation du patrimoine
- Technologie laser
- Ingénierie et fabrication
]








